Last edit: 25/08/2025
The new edition of NFPA 70, or NEC 2017, was published in August 2016 and is valid for the 2017-2020 three-year period.
This important document (over 800 pages) details the design and construction requirements for electrical systems in the United States.
Several new articles are included in the 2017 edition of the NEC, including the following:
- Article 425 – Fixed Resistance and Electrode Industrial Process Heating Equipment
- Article 691 – Large-Scale Photovoltaic (PV) Electric Supply Stations
- Article 706 – Energy Storage Systems (ESS)
- Article 712 – Direct Current Microgrids
The content of these articles is described below.
Article 425 : Fixed Resistance and Electrode Industrial Process Heating Equipment
Article 425 provides requirements for equipment for industrial heating processes involving the use of electric resistors and electrodes. Such equipment must be listed, and the branch circuit into which it is installed must be appropriately sized. It also specifies the installation procedures for such equipment, such as location, operating space, and any protective measures to be adopted.
Article 691: Large-Scale Photovoltaic (PV) Electric Supply Stations
Article 691 concerns the installation of photovoltaic systems with a generation capacity exceeding 5000 kW, defining the requirements for the design, construction and commissioning of such systems.
Article 706: Energy Storage Systems (ESS)
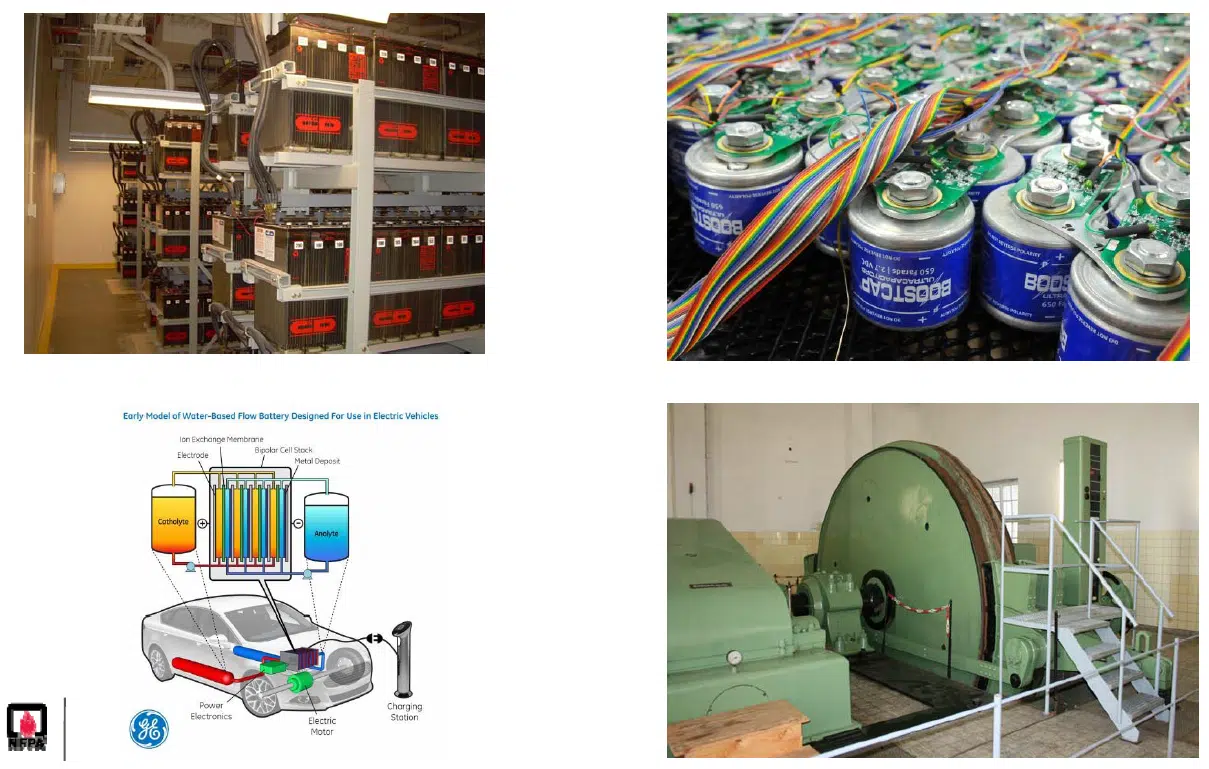
Of particular note is Article 706 , which concerns Energy Storage Systems (ESS). It covers all permanently installed systems, including devices with electrochemical (e.g., batteries), electrolytic (e.g., capacitor banks), and devices that store kinetic energy (e.g., compressed air).
Part 1 of the Article provides general requirements, such as the scope and various definitions. In particular, it establishes that all equipment for such storage systems must be “listed.” Details are provided on the switching devices (switches, disconnectors, etc.) to be used, particularly which system conductors must be capable of being equipped with a switching device.
Part 2 specifically addresses the circuits of energy storage systems, particularly their sizing (conductor capacity, overcurrent protection, and sizing of conductors to the loads powered by these systems) and the maximum current that can flow.
Parts 3, 4 and 5 are specific for electrochemical (which can cause problems due to the corrosive acid contained within them), electrolytic and kinetic storage systems respectively.
Article 712: Direct Current Microgrids
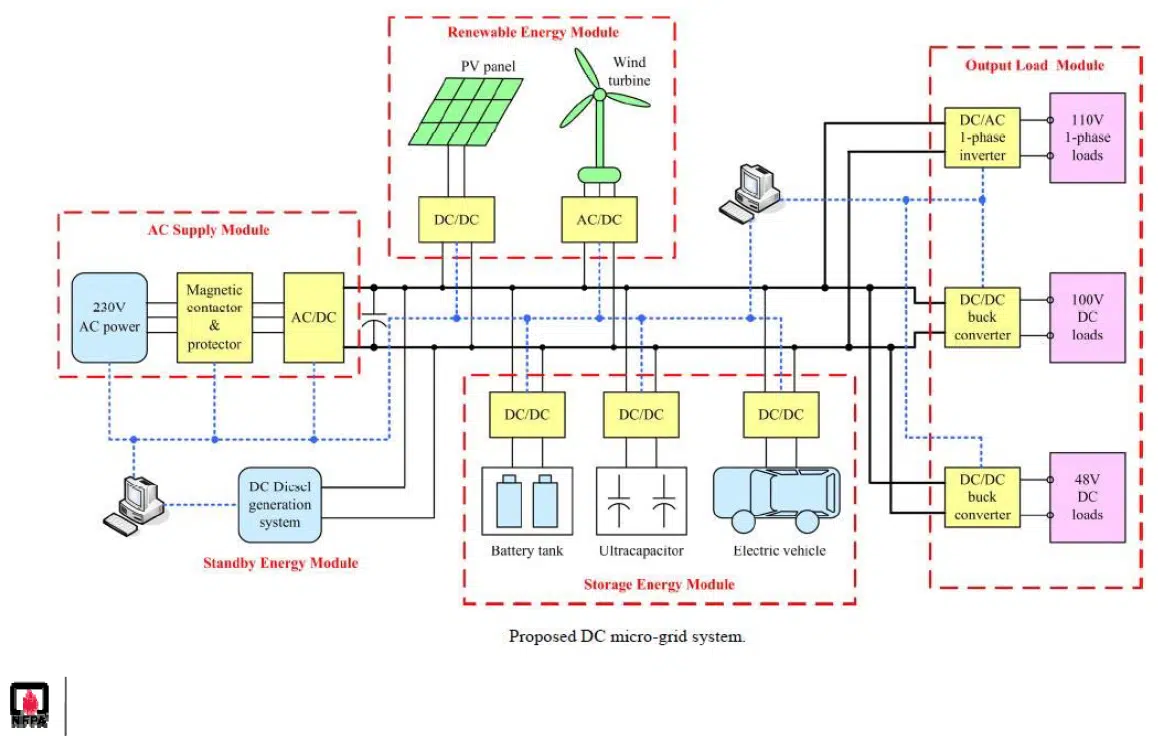
Article 712 , composed of 9 parts, deals with direct current (DC) distribution systems, including the DC power source, DC-to-DC converters, DC loads, and AC loads powered by DC-to-AC inverters.
Part 1 , as always, contains general requirements and definitions. It also specifies that any devices and equipment used must be listed and approved for DC use.
Part 2 contains circuit requirements such as feeder and branch circuit conductor sizing and system voltage ratings.
Part 3 deals with circuit breakers and their proper placement on the system conductors.
Part 4 details wiring methods and identification of live conductors, system earthing, and ground fault and arc flash protection for the entire DC system.
Part 5 concerns the plates to be affixed to the DC system.
Part 6 discusses protective devices and specifies the sizing of overcurrent protectors, interrupting capacities and Short Circuit Current Rating (SCCR).